Hand osteoarthritis can significantly impact your daily life, making simple tasks like gripping a pen or opening a jar feel painful and challenging. Hand osteoarthritis affects the cartilage in the fingers and thumbs, causing stiffness, swelling, and discomfort. Early identification of symptoms and an understanding of the underlying causes are essential for managing the condition. Fortunately, a variety of treatments can help alleviate pain and improve mobility, allowing individuals to maintain an active lifestyle.
What Is Hand Osteoarthritis?
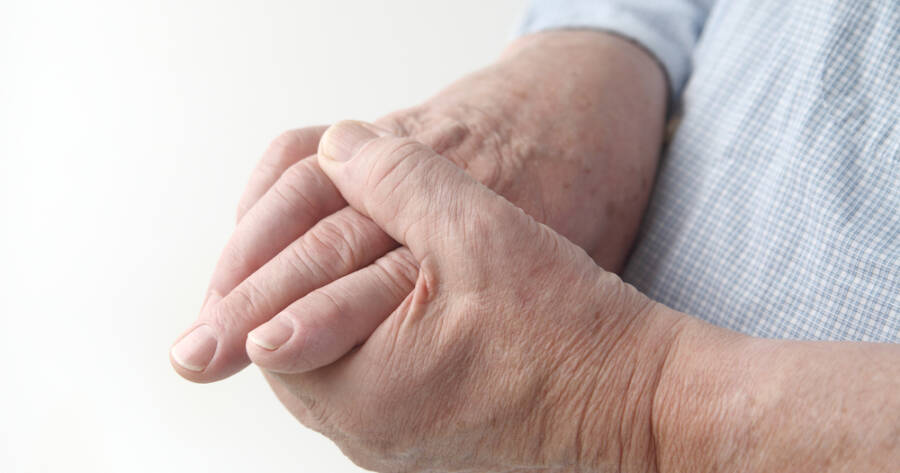
Hand osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease that affects the cartilage in the fingers and thumb, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling. The condition is more common as people age, with women being particularly susceptible. OA can affect different joints in the hand, including the base of the thumb, the joints closest to the fingertips, and the middle joint of the fingers. Over time, the cartilage breaks down, and bones rub together, causing discomfort. OA is a progressive disease, and while there is no cure, treatments can manage the symptoms and help maintain hand function.
Understanding the specific areas where OA occurs can be key to managing the condition. For example, the thumb joint, known as the carpometacarpal (CMC) joint, is often affected, leading to limited motion and difficulty grasping objects. This makes early detection and proper treatment important in slowing the progression of the disease.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
The symptoms of hand osteoarthritis can vary from mild to severe. Early signs include intermittent pain and stiffness, especially in the morning, which eases with rest. As the condition progresses, pain becomes more constant, and you may notice a grinding or clicking sensation in the joints (crepitus). Swelling around the affected joints, the formation of bony lumps (nodes), and loss of hand strength are common as well. Nodules called Heberden’s nodes and Bouchard’s nodes often develop, especially near the finger joints, making them visibly deformed.
Loss of motion is another key symptom. Individuals with hand OA may experience difficulty fully opening or closing their fingers, which can interfere with daily tasks such as writing, eating, or opening containers. It’s crucial to recognize these early warning signs and seek treatment to prevent further joint damage.
What Causes Hand Osteoarthritis?
While the exact cause of hand osteoarthritis is not fully understood, several factors contribute to the development of the condition. Age is a major risk factor, as the cartilage naturally breaks down over time. Women are more prone to developing hand OA, likely due to hormonal factors and structural differences in their hands. Genetics also play a role, as a family history of OA can increase the risk.
In addition to natural aging and genetics, previous hand injuries, such as fractures or joint dislocations, can increase the likelihood of developing OA later in life. Overuse of the hands in repetitive tasks or jobs that require heavy lifting or gripping can also contribute to the condition. Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce strain on the joints and lower the risk of developing OA.
Treatment Options for Hand Osteoarthritis
While there is no cure for hand osteoarthritis, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Non-drug treatments are often recommended first, including physical therapy and joint protection strategies. Wearing a splint or brace can help reduce strain on the affected joints, while hand exercises can maintain flexibility and strength. Heat or cold therapy may provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
If symptoms persist, medications may be prescribed. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can reduce pain and inflammation. For more severe cases, corticosteroid injections into the affected joints may provide longer-lasting relief. In extreme cases where conservative treatments fail, surgical options such as joint replacement or fusion may be considered to improve function and reduce pain.
Managing Hand Osteoarthritis for Better Quality of Life
While hand osteoarthritis can present significant challenges, it’s important to remember that with early intervention and proper management, you can maintain an active and fulfilling lifestyle. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options available can help you take proactive steps in managing the condition. By utilizing a combination of non-drug treatments, medication, and in some cases, surgical intervention, it’s possible to reduce pain, maintain function, and improve your overall hand mobility. Consult with a healthcare provider to develop a tailored treatment plan that works for you.