Dementia tests are crucial tools for detecting early signs of cognitive decline and guiding timely intervention strategies. As dementia cases are projected to increase worldwide, understanding the importance of these assessments becomes essential for proactive health management. From memory and language evaluations to neuropsychological screenings and informant-based questionnaires, a range of testing methods provide valuable insights. Early diagnosis can lead to better treatment planning, improved quality of life, and essential support for patients and families.
Understanding Dementia Tests
Dementia tests are crucial tools in identifying and understanding cognitive impairments, which often manifest as memory issues, personality changes, or unexplained health deterioration. These tests can assist in determining whether patients need additional comprehensive evaluations to diagnose cognitive impairments. Early detection of dementia is essential as it allows for timely intervention, better planning, and participation in clinical studies, all of which can significantly impact the course of the disease.
The Importance of Early Detection
The significance of early dementia detection cannot be overstated, especially as the prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias rises due to the aging population. By 2050, a projected three-fold increase in dementia cases underscores the urgency of early detection. Catching dementia in its early stages opens up possibilities for interventions that can modify lifestyle factors to slow its progression. These factors include diet and exercise modifications, enabling individuals to maintain a better quality of life for a longer period.
Methods of Dementia Screening
Dementia screening employs several methods, each with its unique strengths and limitations. Popular tests like the Mini-Mental State Exam (MMSE) and the Mini-Cog test provide quick, performance-based evaluations but may lack early-stage sensitivity due to cultural biases. Alternatively, informant-based assessments, such as the AD8 and Quick Dementia Rating System, rely on observations from family or friends and are considered effective in detecting cognitive changes unnoticed by the patients themselves.
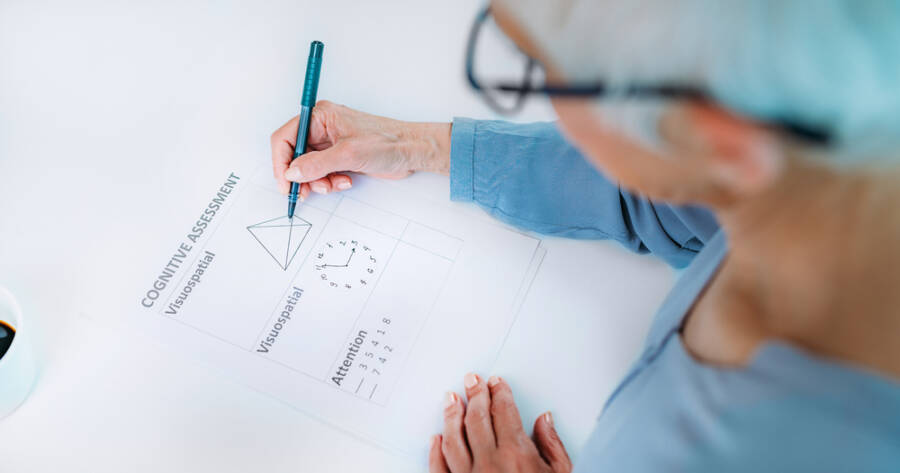
Cognitive Assessment Tools
A myriad of cognitive assessment tools is also available for detecting dementia, each tailored to address different aspects of cognition. The Self-Administered Gerocognitive Exam (SAGE), for example, is an innovative tool developed to detect early signs of cognitive impairments at a higher sensitivity than traditional tests like the MMSE. SAGE is self-administered, requires minimal equipment, and can easily be completed at home, providing an accessible option for individuals seeking initial screening.
Informant Contributions in Assessments
Consideration of input from individuals close to patients is vital in comprehensive dementia assessments. This approach is encapsulated in the Informant Questionnaire on Cognitive Decline in the Elderly (IQCODE), which captures changes in cognitive abilities over a longer period by collecting insights from relatives or caregivers. This technique helps reduce biases related to education or cultural background, which might skew performance-based test results.
Benefits of Early Diagnosis
Receiving a dementia diagnosis early on can be advantageous, offering patients and families the chance for effective planning, resource access, and involvement in care decisions. It can also help address and potentially change lifestyle factors that might affect the disease’s progression. This strategic intervention might include dietary changes, cognitive exercises, or mental health treatment, overall enhancing the patient’s quality of life and prolonging cognitive functionality during the disease progression.
Why You Should Learn More About Dementia Testing Today
Dementia testing serves as a critical gateway to understanding and managing cognitive impairments effectively. As the number of dementia cases is anticipated to increase, having a comprehensive grasp of the different types and benefits of early detection can contribute significantly to better health outcomes. By committing to deeper engagement with both formal assessments and informal observations from close acquaintances, individuals can harness the full potential of early intervention, ensure timely and appropriate medical care, and maintain a greater quality of life amidst cognitive challenges.
Sources
Exploration of Dementia Cognitive Assessment
Impact of Early Detection on Dementia
Comprehensive Guide on Dementia Screening Tools